Proteomics > Which service should I request? > Proteome Identification and Quantification > Mass Spectrometry Imaging
IMPORTANT: THE WORKFLOW IS UNDER DEVELOPMENT
1. Freezing tissue
2. Embedding tissue (optional)
3. Preparing tissue sections
4. Matrix application
FGCZ has 2 instruments that can be used for MS Imaging experiments:
Matrix sprayer
Our current matrix application is based on wet matrix spraying using a versatile and automated MALDI matrix deposition system: HTX M5 Sprayer™. Very thin matrix layers consisting of small crystals can be generated, allowing a spatial resolution of down to 10μm, in some cases even 5μm.
Data analysis
Check the Spatial Transcriptomics pages for other approaches offered at FGCZ.
Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MSI)
Table of contents
IMPORTANT: THE WORKFLOW IS UNDER DEVELOPMENT
General description
The study of biological systems and their function greatly benefits from flexible analysis of multiple molecular entities in a spatially resolved manner, to identify different cell types, monitor cell state and function, understand spatial organization and probe the physical and biochemical interactions of individual cells. Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI), a technique that advanced dramatically in recent years, is ideal for this type of studies: it allows the rapid and sensitive analysis of the distribution of hundreds of peptides, proteins, small molecules, lipids and glycans directly in biological tissue slices.Applications
MSI find applications in almost every field, with typical examples in human and animal clinical applications (i.e. histopathology, drug discovery, analysis of tissue microenvironment), or microbiology (i.e. host-pathogen interactions).- lipids
- small molecules
- glycans
- peptides
- MALDI-IHC-MS
- ....
Workflow
MALDI imaging of tissue requires a tight coordination of tissue sample preparation and MS data acquisition. Our workflow is based on the following common steps. Steps carried out at the FGCZ are highlighted in bold:1. Freezing tissue
2. Embedding tissue (optional)
3. Preparing tissue sections
4. Matrix application
- Matrix chemicals and spraying conditions are optimized and adapted for the analyte(s) of interest. MALDI Matrices are highly purified, recrystallized reagents with the most common ones being:
- DHB (2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid)
- CHCA (α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid)
- DHAP (2,5-Dihydroxyacetophenone).
- Is optimized for the analyte of interest with respect to laser, mass range and ion mobility settings
- MS/MS can be done on targeted masses for identity confirmation
- Imaging data are converted to the open .imzML format and processed (normalization, filtering, segmentation/clustering etc, feature extraction, basic statistical comparisons) with:
- SCiLS™ Lab
- Customized scripts currently under development
- Analyte annotation, in particular for lipids and metabolites can be incorporated
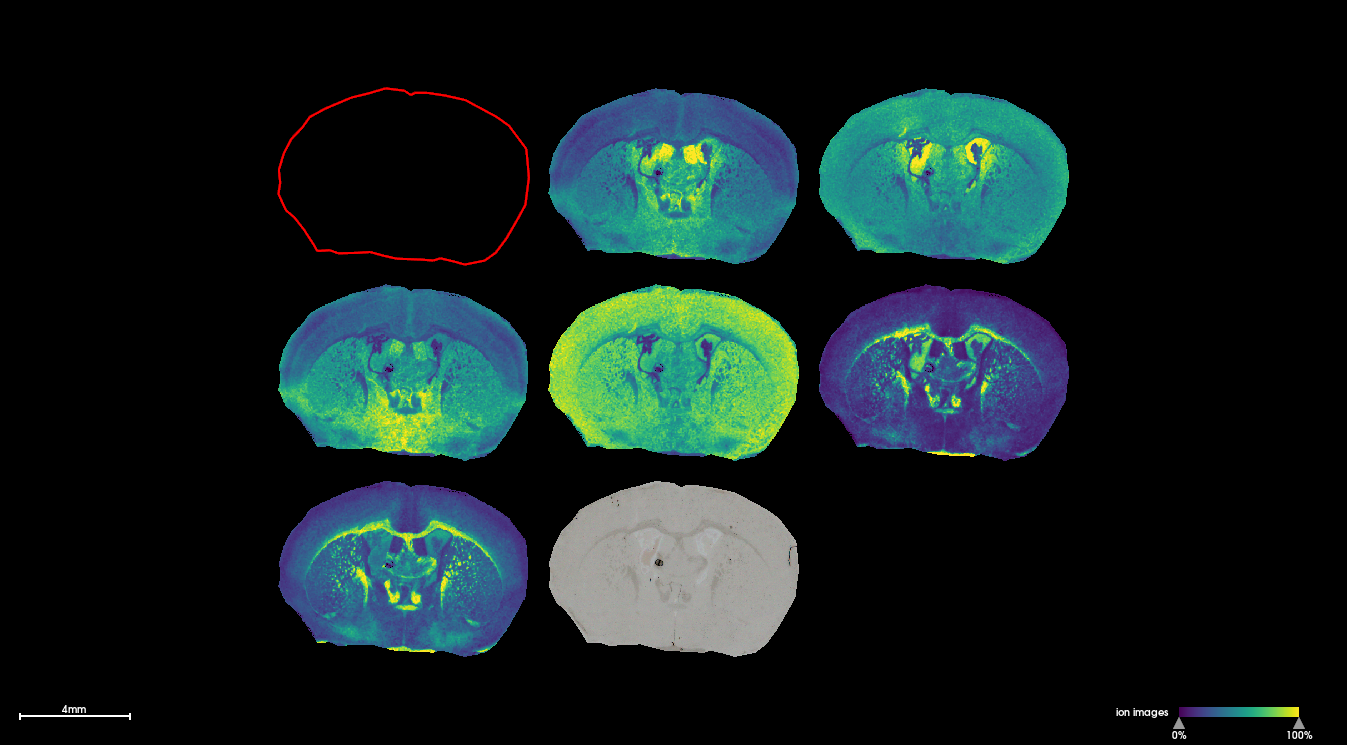
Example
The following image shows selected masses detected in fresh frozen coronal mouse brain sections which correspond to Sphingomyelin, Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphorylethanolamine species. The image was acquired on a timsTOFflex instrument at 20μm spatial resolution.
Instruments @FGCZ
MALDI MS InstrumentsFGCZ has 2 instruments that can be used for MS Imaging experiments:
- rapifleX MALDI tissuetyper (Bruker)
- timsTOF fleX MALDI-2 with microGRID (Bruker)
Matrix sprayer
Our current matrix application is based on wet matrix spraying using a versatile and automated MALDI matrix deposition system: HTX M5 Sprayer™. Very thin matrix layers consisting of small crystals can be generated, allowing a spatial resolution of down to 10μm, in some cases even 5μm.
Requirements and considerations
Tissue and sections preparation:- It is crucial to tightly coordinate tissue extraction, freezing and sectioning with the FGCZ to ensure compatible conditions BEFORE preparing the samples
- FGCZ and UZH Microscopy ZMB are implementing methods for the preparation of tissues for MS Imaging
- Fresh frozen tissue is generally considered best for MALDI-MSI inparticular for lipids and small molecules
- Ideally without any embedding medium if ~10μm sections can be cut and mounted onto the slides without compromising the tissue structure
- If embedding medium is needed, CMC or gelatin can be used. the common embedding medium OCT is NOT compatible due to the high background generated during data acquisition
- Sections need to be mounted on specific conductive glass slides (ideally Bruker MALDI IntelliSlides)
- FFPE samples:
- Typically used for the detection of peptides
- Detection of other analytes such as lipids and small molecules is incomaptible in most cases due to extensive sample processing
- Workflow under development (sections are about 5μm thick)
- Please see Handbook Imaging for more detailed information
- MS imaging can also be carried on other sample types such as cells, organoids or biofilms. Often, these targets require customized approaches regarding embedding media and molds
Data analysis
- The data analysis pipeline is currently under development focussing on:
- Targeted extraction and analysis of a selected number of m/z values
- Etablishing a discovery-type pipeline including database annotation for metabolites and lipids
Other spatial technologies
Spatial multiomics technologies are rapidly evolving. Please contact us at proteomics at fgcz.ethz.ch to inquire about information regarding the most recent additions and future developments.Check the Spatial Transcriptomics pages for other approaches offered at FGCZ.